Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Asai, Masato
Radioisotopes, 67(6), p.291 - 298, 2018/06
Stability and limit of existence essentially depend on nuclear shell structure. It is theoretically predicted that stable doubly-closed-shell spherical superheavy nuclei should exist around the region of the proton number 114 to 126 and the neutron number 172 to 184, although their locations and degree of stability have not been established because of large variety of theoretical predictions. On the other hand, recent advances on experimental techniques have made it possible to accumulate experimental data concerning the shell structure of superheavy nuclei, such as half-lives and nuclear masses. In addition, some pioneering experiments have been performed to directly establish the level structure of superheavy nuclei through spectroscopic methods. This paper introduces the current status of experimental studies on nuclear shell structure of superheavy nuclei.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Koura, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Takahiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 60(9), p.717 - 724, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Ichikawa, Takatoshi; Iwamoto, Akira
Physical Review C, 71(6), p.067601_1 - 067601_4, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Nuclear)We estimate the decrease of the Coulomb-barrier height between colliding parters due to charge polarizations in the entrance channel for cold-fusion reactions. Since the Coulomb-repulsion force increases with increasing the proton numbers of the target and projectile such as cold-fusion reactions, it is expected that the charge distribution of the colliding nuclei is changed to some extent. The resulting charge distribution induced by this polarization decreases the interacting Coulomb energy between the colliding partners, whereas their own self energies increase due to the increase of the symmetry energy. We assume that the resulting charge displacements between protons and neutrons are the sum of the surface- and volume-charge components and estimate the extent of the charge polarization with the self energy on the basis of the droplet model. We show the difference between the charge polarization of light and heavy nuclei and the decrease of the Coulomb barrier height for synthesizing superheavy elements.
Koura, Hiroyuki
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.38, P. 9, 2005/05
We calculate proton-emission partial half lives and discuss dominant decay modes in the heavy and superheavy nuclidic region. The proton-emission partial half-lives are calculated from the one-dimensional WKB method with single-proton potentials and a mass formula that our group has developed. The calculated half lives well reproduce experimental ones in order of 100 or 1/100 which is similar predictability to other predictions as the alpha decay and the beta decay. We apply this result to calculation of branching ratios of nuclear decays considered the alpha decay, beta decay and spontaneous fission in the heavy and superheavy nuclide region. In this analysis we point out that proton-emitting nuclei are expected to be in the unknown proton-rich nuclidic region with 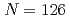 . On the other hand, proton-rich nuclei with
. On the other hand, proton-rich nuclei with 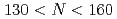 have much shorter spontaneous-fission half-lives than ones of proton emissions on this calculation, therefore we conclude that ground-state proton emissions would not occur in that region.
have much shorter spontaneous-fission half-lives than ones of proton emissions on this calculation, therefore we conclude that ground-state proton emissions would not occur in that region.
Ichikawa, Takatoshi; Iwamoto, Akira; M ller, P.*; Sierk, A. J.*
ller, P.*; Sierk, A. J.*
Physical Review C, 71(4), p.044608_1 - 044608_11, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:89.8(Physics, Nuclear)We estimate the effective fusion barrier in the entrance channel in cold-fusion reactions in a model where the projectile deformation and quadrupole zero-point vibrational energy are taken into account. The effective fusion-barrier height is defined as the barrier energy at the target and projectile separation distance where the system becomes unstable with respect to projectile deformation. We also calculate five-dimensional potential-energy surfaces for the single compound system. For heavy systems the fusion barrier at touching becomes lower than the fission barrier just beyond the ground state of the compound system. Except for reactions in which the projectile is doubly magic or near doubly magic, the calculated quantities are consistent with the observed optimal energies for evaporation-residue formation.
Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Tanikawa, Masashi*; Zhao, Y. L.*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Nakahara, Hiromichi
Physical Review C, 70(1), p.014609_1 - 014609_10, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:66.77(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Zhao, Y. L.*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sueki, Keisuke*; Goto, Shinichi*; Tanikawa, Masashi*; Nakahara, Hiromichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 255(1), p.67 - 72, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.59(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Toshiki; Bonasera, A.*; Papa, M.*; Chiba, Satoshi
European Physical Journal A, 14(2), p.191 - 197, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:77.59(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Poenaru, D. N.; Nagame, Yuichiro; Gherghescu, R. A.*; Greiner, W.*
Physical Review C, 65(5), p.054308_1 - 054308_6, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:96.31(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Suehiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Yoshida, Tadashi
JAERI-Conf 2000-019, p.105 - 108, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Asai, Masato; Sakama, Minoru*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Haba, Hiromitsu; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Goto, Shinichi*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Oura, Yasuji*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 561, p.358 - 367, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Nagame, Yuichiro; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shinohara, Atsushi*
Radioisotopes, 49(7), p.363 - 375, 2000/07
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Akira; M ller, P.*; J.R.Nix*; *
ller, P.*; J.R.Nix*; *
Nuclear Physics A, 596, p.329 - 354, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:92.17(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
;
JAERI 1158, 144 Pages, 1968/03
no abstracts in English